Ann Arbor (Informed Comment) – The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Agency announced Friday that the winter of 2023-24 was the hottest on record in U.S. history. Global records have been kept since about 1850, with the widespread use of mercury thermometers.
The average surface temperature of the US this past winter was 37.6°, which is 5.4° F. above the norm. A winter that is 5 degrees warmer than normal ought to be horrifying. This is not normal. And we are only at the beginning of this heating.
One way you could tell it was hot was that Wisconsin had its first February tornado on record. Wisconsin.
Another way you could tell that it was a hot, hot winter was that Texas experienced the largest and most destructive wildfires in the past 20 years, and likely in the state’s recorded history. The Smokehouse Creek Fire merged with another huge conflagration and burned 1,075,000 acres in Texas and Oklahoma, making it the second largest fire in US history. It is still only 75% contained. In the Texas Panhandle, at least 10,000 cattle have been killed or so badly injured they’ll have to be euthanized, while many grain production companies reported “total losses,” according to CBS News. Hundreds of homes have been destroyed, and two people killed.
Wildfires are common in Texas in the summer, and occur as early as March in the Panhandle, but to have so much of the state aflame in February is, let us say, unusual.
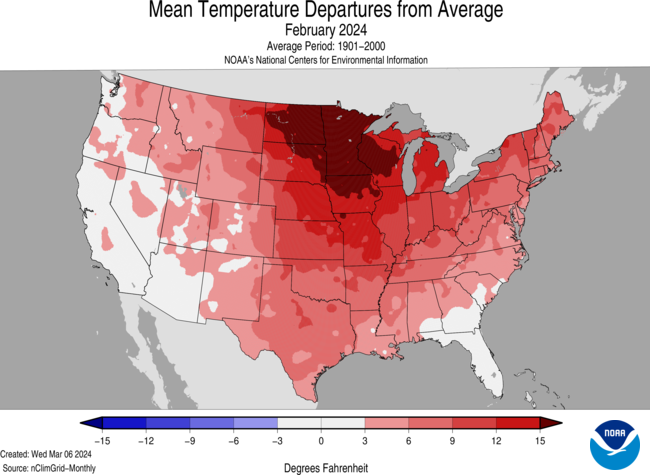
But it isn’t just Texas. The United States of America was lit up like a Christmas tree in February, with unusually high temperatures. Consider this temperature map for February:
Then there were a series of atmospheric rivers that inundated California, causing widespread flooding and destruction. Phys.org notes, “At one point, weather agencies posted flood watches for nearly the entirety of California’s coast.” As we heat up the earth, we cause more water to evaporate from the oceans, making the atmosphere denser with moisture. Ribbons of moisture move from the equator up to the temperate zones and dump their water. Climate change increases the rainfall released and also changes the patterns of the atmospheric rivers.
In 2023, the US had twenty-eight disasters costing a billion dollars or more. During the past 40 years, the average number of billion-dollar climate disasters per annum was only 8.5. But in the past 5 years the average has been about 20 such very costly catastrophes. The rate of catastrophe is sky-rocketing.
This finding is yet another indication that global heating is proceeding at least as fast as climate scientists projected at the beginning of our century, and in many cases much faster. Climate risks becoming chaotic if we heat up the earth’s surface more than 2.7° F. (1.5° C.) above the preindustrial average. We’ve already heated it up to around 2.1° F. higher than that 18th century average, by spewing billions of metric tons of carbon dioxide, a heat-trapping gas, into the atmosphere. We’re wrecking the earth by burning coal for heat and electricity, or fossil gas, or by burning petroleum in automobiles and trucks. We still aren’t reducing the amount of CO2 we put into the atmosphere annually, though its increase has leveled off. We have to cut it out. Now.



 © 2025 All Rights Reserved
© 2025 All Rights Reserved